The genetic architecture of amino acids dissection by association and linkage analysis in maize
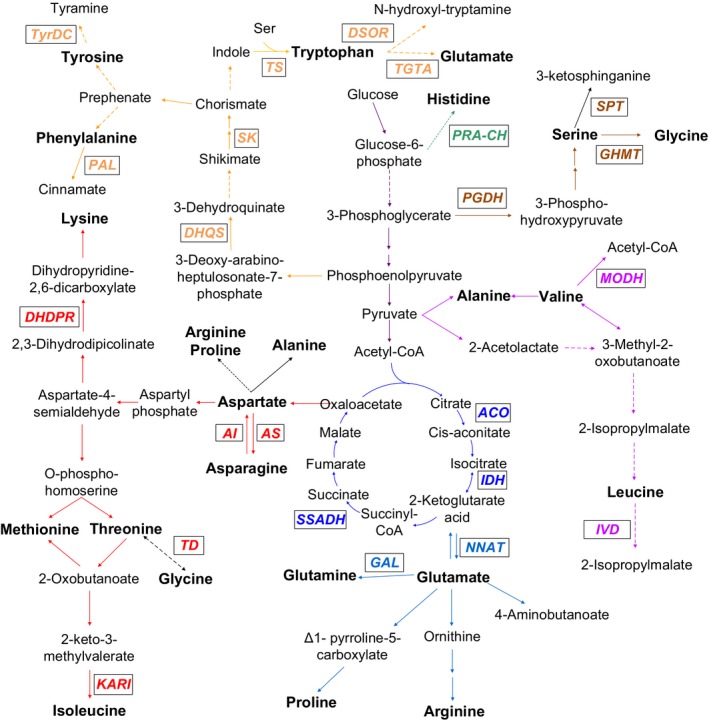 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: Unsplash
Abstract
Amino acids are both constituents of proteins, providing the essential nutrition for humans and animals, and signalling molecules regulating the growth and development of plants. Most cultivars of maize are deficient in essential amino acids such as lysine and tryptophan. Here, we measured the levels of 17 different total amino acids, and created 48 derived traits in mature kernels from a maize diversity inbred collection and three recombinant inbred line (RIL) populations. By GWAS, 247 and 281 significant loci were identified in two different environments, 5.1 and 4.4 loci for each trait, explaining 7.44% and 7.90% phenotypic variation for each locus in average, respectively. By linkage mapping, 89, 150 and 165 QTLs were identified in B73/By804, Kui3/B77 and Zong3/Yu87-1 RIL populations, 2.0, 2.7 and 2.8 QTLs for each trait, explaining 13.6%, 16.4% and 21.4% phenotypic variation for each QTL in average, respectively. It implies that the genetic architecture of amino acids is relative simple and controlled by limited loci. About 43.2% of the loci identified by GWAS were verified by expression QTL, and 17 loci overlapped with mapped QTLs in the three RIL populations. GRMZM2G015534, GRMZM2G143008 and one QTL were further validated using molecular approaches. The amino acid biosynthetic and catabolic pathways were reconstructed on the basis of candidate genes proposed in this study. Our results provide insights into the genetic basis of amino acid biosynthesis in maize kernels and may facilitate marker-based breeding for quality protein maize.