 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: Unsplash
Abstract
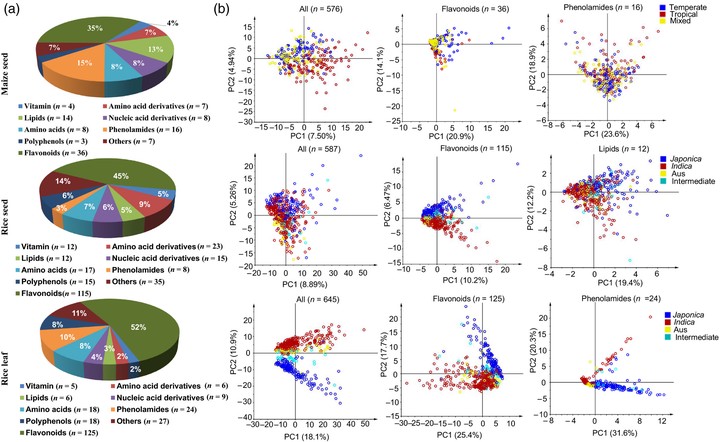
Metabolites are the intermediate and final products of metabolism, which play essential roles in plant growth, evolution and adaptation to changing climates. However, it is unclear how evolution contributes to metabolic variation in plants. Here, we investigated the metabolomics data from leaf and seed tissues in maize and rice. Using principal components analysis based on leaf metabolites but not seed metabolites, metabolomics data could be clearly separated for rice Indica and Japonica accessions, while two maize subgroups, temperate and tropical, showed more visible admixture. Rice and maize seed exhibited significant interspecific differences in metabolic variation, while within rice, leaf and seed displayed similar metabolic variations. Among 10 metabolic categories, flavonoids had higher variation in maize than rice, indicating flavonoids are a key constituent of interspecific metabolic divergence. Interestingly, metabolic regulation was also found to be reshaped dramatically from positive to negative correlations, indicative of the differential evolutionary processes in maize and rice. Moreover, perhaps due to this divergence significantly more metabolic interactions were identified in rice than maize. Furthermore, in rice, the leaf was found to harbor much more intense metabolic interactions than the seed. Our result suggests that metabolomes are valuable for tracking evolutionary history, thereby complementing and extending genomic insights concerning which features are responsible for interspecific differentiation in maize and rice.