A genetic and metabolic roadmap to fresh flavor of waxy maize
Introduction
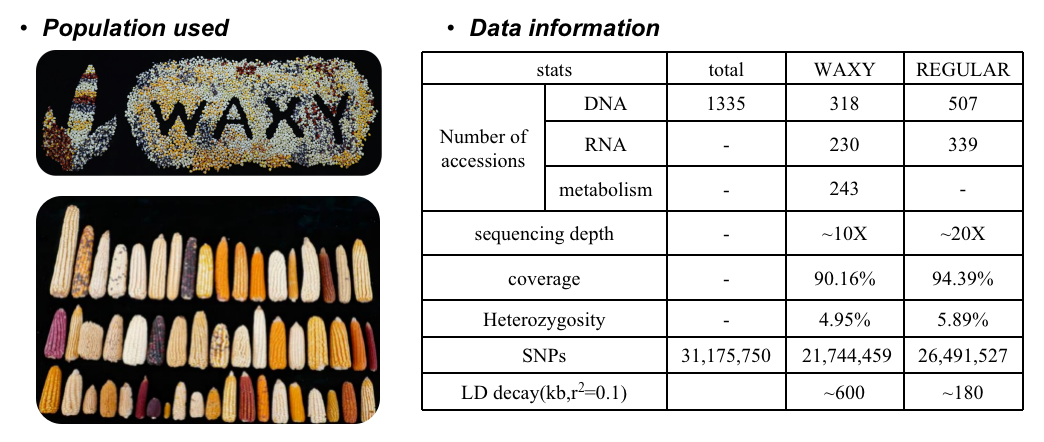
Waxy maize (Zea mays L. sinensis Kulesh), a popular fruit and vegetable crop as well as an important source of micronutrients in the human diet, has experienced domestication selection and subsequent genetic improvement during its long cultivation history, exhibiting significant divergence from modern regular maize. Comparative omics analyses between 318 waxy maize and 507 modern regular maize inbred lines revealed obviously divergence between waxy and regular maize. In order to deeply explore the metabolic basis of the flavor of waxy maize, over 1600 metabolites are qualified in the waxy maize population. Of which, totally 84 key metabolites were identified to significantly contribute to the fresh flavor of waxy maize based on a 100-people tasting experiment. These flavor-associated metabolites involved in sugar and sugar derivatives, amino acid-related and some secondary metabolites, a total of 458 candidate genes were discovered using genome-wide association study. These flavor-associated metabolites and key genes could explain totally 74% of the variation of waxy maize flavor. Our findings shed lights on the historical selection of waxy maize, demonstrate the genetic and metabolic basis of the fresh flavor of waxy maize, which provides useful resources and knowledge for the high nutritional maize breeding.
The high-density variant map of waxy and regular population
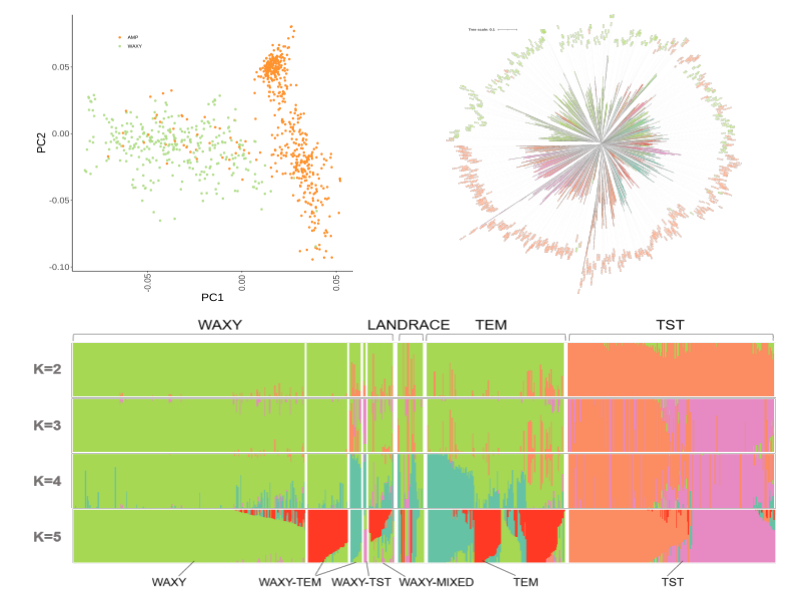
Population structure of waxy and regular population
- Waxy and regular maize population are relatively independent, and only a few materials “mixed”.
- The genetic distance is closer between waxy maize with temperate maize lines compared to tropical ones.
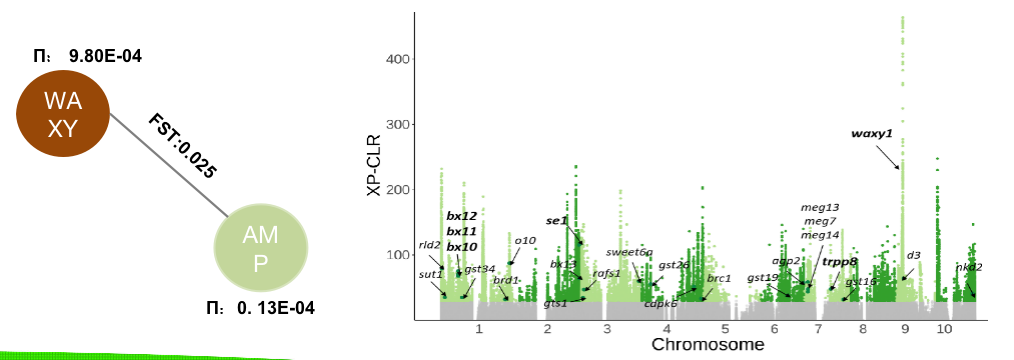
Divergence on genomic and transcriptional level
- The fixation index value between two panel was 0.025, suggesting the obvious divergence.
- ~39M regions were identified.
- 4462 genes were selection candidates.
- 3365 genes were found differentially expressed in two panels.
Divergent pathways
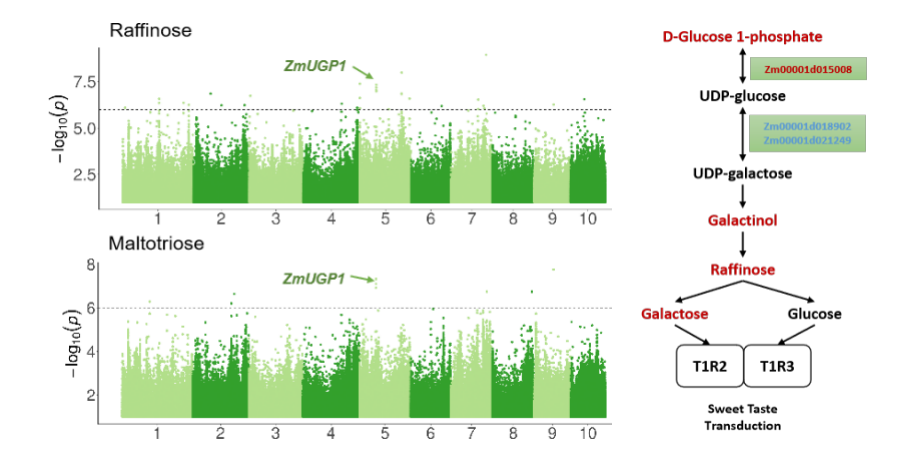
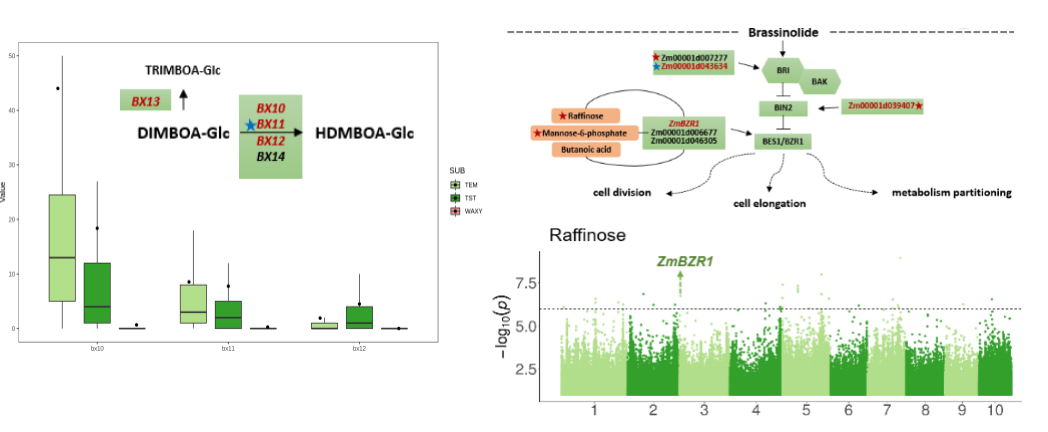
Besides the famous known gene waxy1 and starch related pathway, many genes and pathways such as benzoxazinoid and brassinosteroid pathways exhibited to be selected during the breeding history of waxy maize. These divergence in metabolic pathways is probably due to artificial selection of flavor-associated traits of waxy maize.
Waxy maize tasting experiment
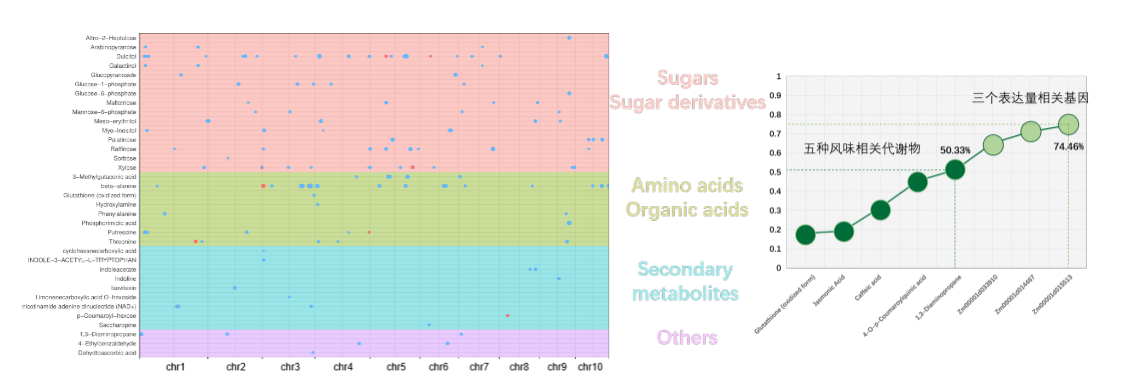
Metabolomics helps to reveal genetic basis of waxy maize flavor
- Over 1600 metabolites are qualified in waxy maize population.
- 84 key metabolites significantly contribute to fresh flavor of waxy maize.
- 458 candidate genes by mGWAS and 2842 expression-flavor-associated genes.
- Explain totally 74% of the variation of waxy maize flavor.
ZmUGP1, a gene influence fresh flavor of waxy maize